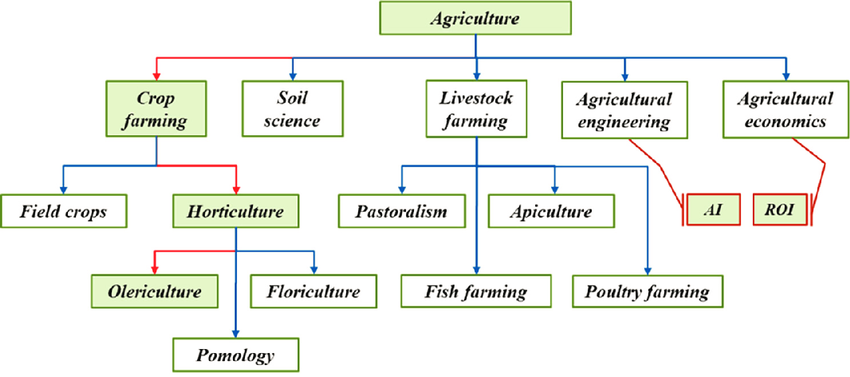
Agriculture is a broad field encompassing various branches or subfields, each focusing on specific aspects of cultivating crops, raising livestock, and managing natural resources related to farming. Here are some major branches of agriculture:
- Crop Agriculture:
- Field Crops: Cultivation of crops like grains (wheat, rice, corn), oilseeds (soybeans, sunflower), and fiber crops (cotton, jute).
- Horticulture: Cultivation of fruits, vegetables, flowers, ornamental plants, and spices.
- Olericulture: Focuses on vegetable cultivation.
- Pomology: Focuses on fruit tree cultivation.
- Livestock Farming:
- Animal Husbandry: Rearing and management of animals for various purposes such as meat, milk, leather, and other products.
- Poultry Farming: Raising birds like chickens, ducks, turkeys for meat and eggs.
- Dairy Farming: Milk production and processing.
- Agricultural Engineering:
- Farm Machinery and Equipment: Design, development, and maintenance of machinery and tools used in agriculture.
- Irrigation Engineering: Design and management of irrigation systems to ensure efficient water use in agriculture.
- Agronomy:
- Soil Science: Study of soils and their properties to optimize crop growth and health.
- Crop Physiology: Study of the physiological processes of crops and their responses to environmental conditions.
- Agroforestry: Integrating trees and shrubs with crops or livestock to create a sustainable and productive agricultural system.
- Agricultural Economics and Agribusiness: Study of economic principles applied to agriculture, including farm management, market analysis, and agricultural policy.
- Agricultural Biotechnology: Application of biotechnological techniques to improve crop and livestock productivity, disease resistance, and genetic modification.
- Agroecology: Integration of ecological principles into agricultural systems to promote sustainability, biodiversity, and environmental health.
- Agricultural Education and Extension: Involves educating farmers and providing them with the latest knowledge, technologies, and practices to improve their productivity and income.
- Agricultural Entomology and Pest Management: Study of insects and other pests that affect crops and methods to manage and control them sustainably.
These branches often overlap and interact to ensure a comprehensive approach to modern agriculture, addressing the diverse needs of farmers, consumers, and the environment.
Buy Book of Coceptual Objective of Agriculture.
